What are the common 8 Causes Of Hearing Loss?
For many people, common Causes of hearing loss can be difficult and isolating. It may interfere with our capacity to interact with our loved ones and cause us to feel angry and depressed. Age-related hearing loss, noise exposure, genetics, illnesses, drugs, trauma, earwax buildup, and other disorders are only a few of the Causes of hearing loss. If you notice changes in your hearing, it’s critical to seek treatment right away because untreated hearing loss can significantly lower your quality of life. Fortunately, hearing loss can be managed with the aid of hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive technologies. Regular hearing examinations and implementing preventative measures, such as donning earplugs or earmuffs in noisy settings, can also assist in preventing hearing loss, Remember, seeking help for hearing loss is a brave and positive step towards improving your well-being.
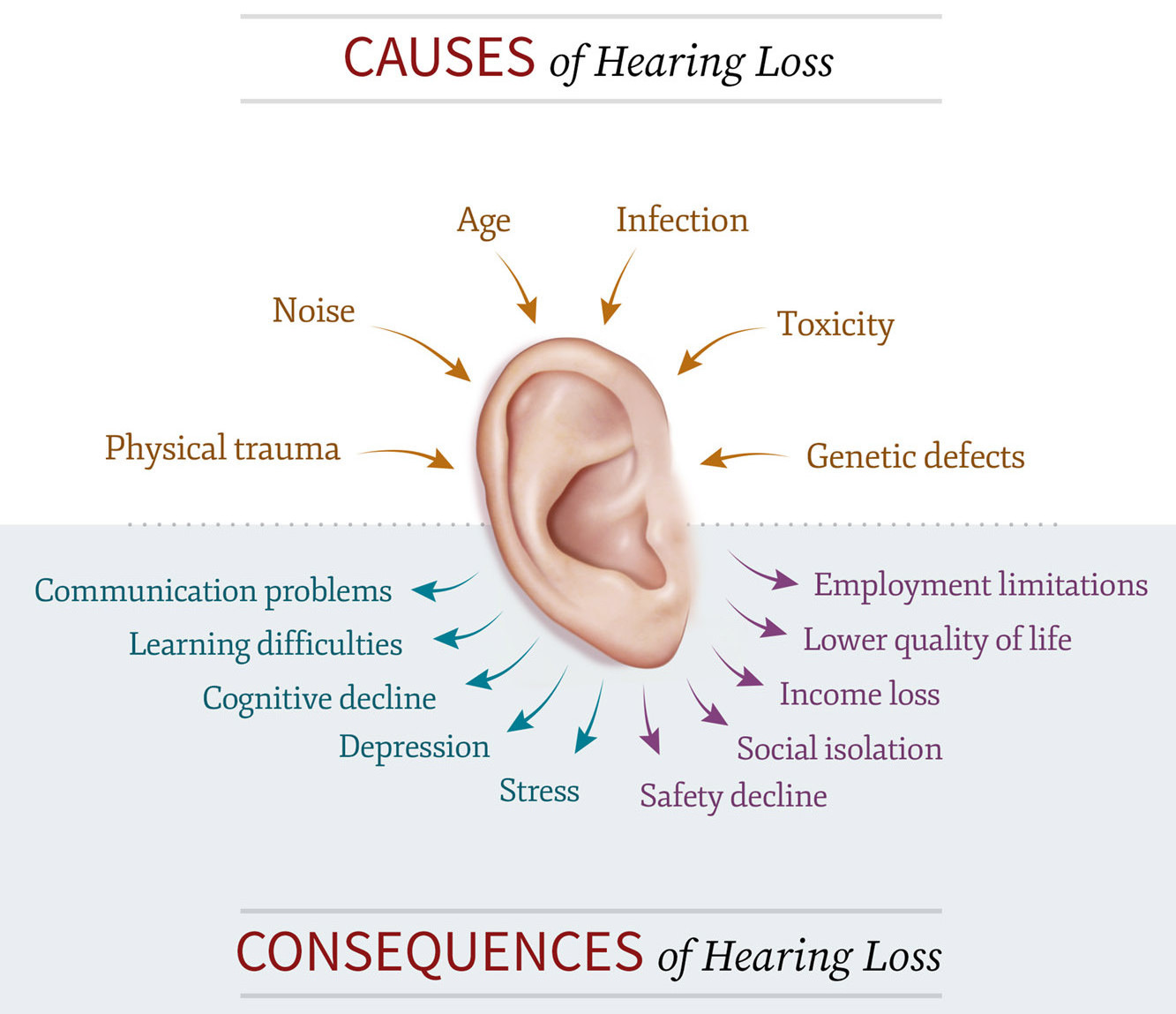
Importance of understanding the causes of hearing loss:
For us to be healthier generally, it is crucial to comprehend the causes of hearing loss. Hearing loss can significantly affect our daily life, resulting in cognitive decline, sadness, and social isolation. Knowing the typical causes of hearing loss will help us prevent or treat it. Hearing loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including ageing, noise exposure, genetics, infections and illnesses, drugs, trauma, earwax buildup, and certain diseases. Knowing the reason for our hearing loss can help us get the right medical care at the right time. Hearing protection measures and routine hearing examinations can both help prevent hearing loss. Don’t let hearing loss prevent you from leading the life you deserve.
Knowing the reasons behind hearing loss might empower us to take charge of our hearing health and enhance our general wellbeing.
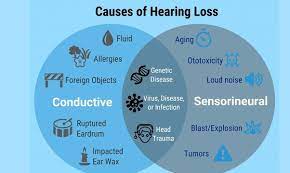
Presbycusis, often known as age-related hearing loss, is a prevalent disorder that affects many older persons. Hearing loss results from the deterioration of the sound-detection cells in our ears as we become older. The disorder can make it difficult to hear high-pitched noises or understand speech in noisy surroundings and normally worsens progressively over time. Presbycusis may also be influenced by genetics, noise exposure, and specific drugs, in addition to age.
Thankfully, there are methods for managing hearing loss brought on by ageing, such as utilizing hearing aids or assistive listening tools. Additionally, you may help avoid additional hearing loss by getting regular hearing exams and taking precautions to safeguard your hearing, like donning earplugs or earmuffs in noisy places. We may take action to manage and avoid age-related hearing loss by being aware of its causes, which will enhance our general hearing health.
Statistics on how many people are affected by it:
A frequent ailment that affects millions of people worldwide is hearing loss. A debilitating hearing loss affects over 466 million individuals globally, and by the year 2050, that figure is projected to reach over 900 million. Only in the United States do half of those over 75 and 1 in 4 adults with ages 65 to 74 have hearing loss. Age-related hearing loss, noise exposure, genetics, illnesses, drugs, trauma, earwax buildup, and other disorders are only a few of the reasons of hearing loss.
If you start to notice changes in your hearing, it’s critical to get medical help right away because untreated hearing loss can significantly lower your quality of life. We may take measures to avoid and manage this illness, resulting in improved hearing health and general wellbeing, by being aware of the prevalence of hearing loss and its main causes.
Presbycusis, often known as age-related hearing loss, is a prevalent disorder that affects many older persons. There are things you can do to prevent or delay hearing loss, even though the condition is frequently a natural part of ageing.
Avoiding loud noises is one of the best methods to ward off hearing loss as you age. When utilizing power tools or in loud venues like stadiums, concerts, or athletic events, wear earplugs or earmuffs. Limit your exposure to loud noise by lowering the volume on your electronic gadgets.
Age-related hearing loss can be avoided by leading a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and abstinence from smoking have all been related to a lower incidence of hearing loss.
For early detection of any hearing loss, routine hearing examinations are crucial. Seek immediate medical assistance if you detect any changes in your hearing, such as difficulties hearing in noisy surroundings or difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds.
Finally, if you operate in a noisy setting, think about adopting hearing protection tools like earplugs or noise-canceling headphones.
You can keep good hearing health well into your senior years by taking precautions to avoid age-related hearing loss.
Noise-induced hearing loss:
-
Explanation of noise-induced hearing loss:
Exposure to loud noises can result in a specific type of hearing loss called noise-induced hearing loss. Long-term exposure to sounds louder than 85 dB can harm the sensitive inner ear hair cells, resulting in hearing loss. This kind of hearing loss can happen suddenly, like after being exposed to an explosion or gunshot, or it can happen gradually after being exposed to loud noises repeatedly, like at music festivals or when using power tools without hearing protection.
By protecting your hearing, noise-induced hearing loss can be avoided. This entails reducing the amount of time you spend in noisy locations, using earplugs or earmuffs when exposed to loud noises, and lowering the volume on your electronic devices.
You must act quickly to get medical help if you think you may have hearing loss brought on by noise. Your quality of life can be improved and additional hearing loss can be avoided with early detection and treatment. You may safeguard your hearing for years to come by being aware of the causes of noise-induced hearing loss and implementing preventative measures.
-
Types of environments that can cause noise-induced hearing loss:
Exposure to loud noises can result in a common type of hearing loss called noise-induced hearing loss. Hearing loss brought on by noise can happen in a variety of settings.
The workplace is one of the settings where noise-induced hearing loss can happen most frequently. Heavy machinery, power tools, and noisy construction sites can expose employees to dangerously high noise levels, which can eventually cause hearing damage.
Concerts and other loud events are another setting where noise-induced hearing loss can develop. At these events, the noise levels can go as loud as 120 dB, which can result in immediate and long-term hearing loss.
Hunting, shooting, and motorsports can all expose people to loud noises that can damage their hearing.
In these situations, it’s crucial to take precautions to safeguard your hearing by donning earplugs or earmuffs, minimizing your exposure to loud noises, and taking pauses in more peaceful locations. You may safeguard your hearing health for years to come by being aware of the settings that can lead to noise-induced hearing loss and taking preventative actions.
-
Prevention tips:
Your quality of life may be significantly impacted by hearing loss, although many cases of hearing loss are preventable. The following preventative advice can help you safeguard your hearing:
- Wear ear protection: It’s important to wear earplugs or earmuffs to preserve your hearing whether you work in a noisy setting, go to concerts or athletic events, or participate in loud activities like shooting or motorcycling.
2. Reduce the volume whether watching TV, listening to music, or using headphones; do this at a safe volume. Generally speaking, the volume is too loud if someone sitting next to you can hear what you’re listening to.
3. Take breaks. If you are subjected to loud noises for an extended amount of time, take frequent breaks in quieter settings to give your ears a break.
4. Regularly check your hearing: Regular hearing examinations can aid in the early detection of hearing loss and assist stop further harm.
5. Limit your exposure to loud noises: If at all possible, avoid or drastically reduce your exposure to loud noises.
You may safeguard your hearing and lower your risk of experiencing hearing loss brought on by noise exposure by using these prevention strategies. Keep in mind that prevention is the key to maintaining a high quality of life, and that this includes taking care of your hearing health.
Genetic causes of hearing loss:
-
Explanation of genetic hearing loss:
Changes in your DNA that impact the growth or operation of your inner ear are the root cause of genetic hearing loss. Syndromic and non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss are the two main forms.
Other illnesses including Usher syndrome, Waldenburg syndrome, or Down syndrome are linked to syndromic hearing loss. In addition to affecting hearing, these diseases can also impair balance, vision, and other body processes.
The most prevalent kind of hereditary hearing loss, non-syndromic hearing loss can be inherited in a dominant, recessive, or X-linked fashion. Non-syndromic hearing loss may occasionally result from an unintentional genetic mutation.
The precise hereditary cause of hearing loss can be determined by genetic testing, which can assist direct treatment choices and provide useful information for family planning.
Although hereditary hearing loss cannot be prevented, it can be managed and treated if it is discovered early through newborn hearing screening and routine hearing exams. In order to understand their risk and make wise health decisions, those with a family history of hearing loss should strongly explore genetic counselling.
-
Types of mutations that can cause it:
Numerous genetic abnormalities that impact the growth and operation of the inner ear can result in hearing loss. Dominant, recessive, and mitochondrial genetic alterations are the three main types that can result in hearing loss.
Dominant mutations, which are typically progressive and result from a single faulty gene from a single parent, decrease hearing with time. Hearing loss that can be present at birth or develop later in life is caused by recessive mutations, which happen when both parents pass on a copy of the defective gene.
Mutations in the mitochondria are inherited from the mother and can lead to a number of health problems, including hearing loss. Genetic testing can pinpoint the precise genetic mutation causing a person’s hearing loss, which can inform treatment decisions and be useful for family planning.
Although hereditary hearing loss cannot be prevented, it can be managed and treated if it is discovered early through newborn hearing screening and routine hearing exams. In order to understand their risk and make wise health decisions, those with a family history of hearing loss should strongly explore genetic counselling.
-
Tips for individuals with a family history of hearing loss:
People who have a family history of hearing loss may be more likely to experience it themselves. There are things people can do to help maintain their hearing and manage the problem if it does manifest itself, even if genetic hearing loss cannot be prevented.
In order to track any changes in hearing ability, it’s crucial to regularly check your hearing. Early detection and treatment can help stop further harm and enhance results.
Additionally, it’s crucial to safeguard hearing in noisy settings by donning earplugs or earmuffs when around loud noises. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as quitting smoking and consuming less alcohol, can also help protect hearing.
Finally, genetic counselling can help people who have a family history of hearing loss better understand their risk and make health-related decisions.
People with a family history of hearing loss can assist protect their hearing and manage the problem if it arises by being proactive and aware of their risk.
Infections and illnesses that can cause hearing loss:
-
Explanation of how certain infections and illnesses can cause hearing loss:
By harming the hearing-related ear structures, several diseases and infections can result in hearing loss. These consist of:
- Ear infections: Middle or inner ear infections can result in swelling and fluid accumulation, which can impair hearing either temporarily or permanently.
- Meningitis: This swelling of the tissues lining the brain and spinal cord can harm the nerves that control hearing.
- Measles, mumps, and rubella are viral illnesses that can harm the inner ear and result in hearing loss.
- Autoimmune diseases: Illnesses including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to ear inflammation, which compromises hearing.
- Ototoxic medications: A number of pharmaceuticals, including several antibiotics and chemotherapy therapies, can have the adverse effect of hearing loss.
Infections or illnesses that could impair hearing should be promptly treated by a physician. In some circumstances, treatment might be able to stop or lessen hearing loss.
-
Examples of infections and illnesses that can cause hearing loss:
A number of disorders and infections have the potential to damage hearing. Among the most typical instances are:
- Otosclerosis: This disorder results in aberrant middle ear bone growth, which can obstruct sound transmission and cause hearing loss.
- Vertigo, ringing in the ears, and hearing loss are all potential symptoms of Meniere’s disease, an inner ear condition.
- The nerve that controls hearing and balance can develop an acoustic neuroma, a benign tumour.
- Syphilis: In its latter stages, this sexually transmitted virus can result in hearing loss.
- Diabetes: People who have diabetes may be more likely to experience hearing loss, probably as a result of blood vessel damage in the ear.
- HIV/AIDS: This infection can harm the inner ear or hearing-related nerves, which can result in hearing loss.
It’s critical to comprehend the possible causes behind hearing loss and to take precautions to preserve your hearing wherever practical. Consult a healthcare provider if you believe you could have hearing loss for a precise diagnosis and the best course of action.
-
Tips for preventing hearing loss from infections and illnesses:
There are steps you may take to minimize your chance of acquiring hearing loss as a result of infections and diseases, even if not all of them can be prevented. Here are some recommendations for avoiding infections and illnesses-related hearing loss:
- Maintain excellent hygiene by regularly washing your hands, especially during the cold and flu season, to lower your chance of being ill.
- Get vaccinated: Immunizations can shield you from diseases like measles and mumps that can impair your hearing.
- Work with your healthcare physician to manage any chronic disorders you may have, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS, in order to reduce your chance of problems like hearing loss.
- Avoid using cotton swabs or other things to clean your ears if you have an ear infection since doing so can force bacteria deeper into the ear canal. Use noise-cancelling headphones or earplugs to shield your ears from loud noises that could result in temporary or permanent hearing loss.
By following these recommendations, you can lower your risk of experiencing infections and illnesses-related hearing loss. To help maintain your hearing and stop future harm, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical assistance if you do experience hearing loss.
Medications that can cause hearing loss:
-
Explanation of medications that can cause hearing loss:
Medication use is just one of the many causes of hearing loss. Hearing loss can result from certain pharmaceuticals, referred to as ototoxic substances, harming the inner ear’s hair cells. Some antibiotics, chemotherapeutic medications, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently ototoxic. These drugs may produce mild, moderate, severe, temporary, permanent, or no hearing loss at all, depending on the individual patient.
Before beginning a new drug, it’s crucial to discuss any potential side effects with your doctor or chemist. Alternative drugs that don’t pose the same risk of hearing loss might be available in some circumstances. Additionally, it’s crucial to get your hearing checked frequently and to let your doctor know if anything changes if you already take a prescription that has the potential to cause hearing loss. You may help safeguard your hearing and avoid hearing loss brought on by medications by being proactive and knowledgeable.
-
Examples of medications that can cause hearing loss:
A typical side effect of some drugs is hearing loss. Ototoxic drugs are those that have the potential to impair hearing. Hearing loss or tinnitus may result from these drugs’ harm to the auditory nerve or inner ear. Certain antibiotics, chemotherapeutic treatments, loop diuretics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are some of the most popular medications that might result in hearing loss.
Not everyone who takes these medications will develop hearing loss, it is crucial to remember. The likelihood of developing hearing loss is affected by variables like dosage, duration of usage, and personal susceptibility.
It’s crucial to discuss any potential side effects with your doctor if you’re taking a medicine that has the potential to cause hearing loss and to get your hearing checked frequently. In rare circumstances, your doctor might be able to replace the medicine you’re taking with one that has fewer negative effects.
-
Tips for discussing medication side effects with a healthcare provider:
Some drugs have a side effect that can cause hearing loss. These substances, also referred to as ototoxic drugs, can impair hearing temporarily or permanently. Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy treatments, and aspirin used in high dosages are a few typical medications that might result in hearing loss.
It is crucial to talk to your healthcare professional if you are taking medication and experience changes in your hearing. They might be able to change the medication you’re taking for you or adjust the dosage. Before beginning a new medicine, it’s vital to talk to your doctor about any hearing loss or associated disorders you may have.
Always read the drug labels and take the prescription as directed. Refrain from exceeding the advised dose or using medications for which you have not received a prescription. Before beginning or stopping any medicine, always with your healthcare professional. You can lessen the likelihood that medication-induced hearing loss will occur by being proactive and open with your doctor about any potential adverse effects.
-
Explanation of how head and ear injuries can cause hearing loss:
Hearing loss can result from head and ear accidents, particularly if the eardrum or the delicate bones inside the ear are injured. An abrupt impact from a head injury, such as one sustained in a vehicle accident, might rupture the eardrum or harm the inner ear. Similar to this, exposure to loud noises like explosions can harm the sensitive ear structures and lead to hearing loss.
It’s crucial to take preventative measures to safeguard your hearing from harm, such as wearing protective equipment during sports or construction activity. Additionally, it’s essential to get medical aid right away if you hurt your head or ears because timely care can help prevent future harm.
Audiologists can assess the extent of the damage and recommend the best course of action if you are experiencing any hearing loss following a head or ear injury. In some circumstances, hearing loss brought on by head and ear injuries may require the use of hearing aids or other assistive technology.
-
Examples of accidents and injuries that can cause hearing loss:
Hearing loss can result from head- and ear-related accidents and injuries. Hearing loss that is either temporary or permanent can arise from such injuries to the auditory nerve or the sensitive ear tissues. Traumatic brain injuries, eardrum ruptures, exposure to abrupt loud noises, and skull fractures are a few incidents and injuries that can result in hearing loss.
Additionally, sports-related injuries like those sustained in boxing, football, and wrestling can result in hearing loss. This is due to the fact that these activities frequently involve contact that could result in a hit to the head and hearing loss.
To avoid head and ear injuries that could result in hearing loss, it is crucial to practice safety measures and put on the proper protective gear, such as helmets. In the event of an injury, go to the hospital right away to get treated properly and stop future harm.
Trauma-related hearing loss is a term used to describe hearing loss brought on by accidents or traumas. Explosions, head injuries, or abrupt exposure to loud noises can all result in this kind of hearing loss. It can also happen when something pierces the ear or skull. Depending on the severity of the injury, hearing loss caused by trauma may be either temporary or permanent.
The greatest strategy for avoiding trauma-related hearing loss is prevention. When working in noisy locations or taking part in activities like shooting or motorsports, it’s important to use protection equipment, such as earplugs or noise-canceling headphones. Additionally, it’s important to adhere to safety precautions and take caution when working with heavy machinery or performing physical activities
Earwax buildup:
-
Explanation of how earwax buildup can cause hearing loss:
Cerumen, often known as earwax, is a natural substance that aids in cleaning and protecting the ear canal. However, a significant amount of earwax buildup can result in hearing loss. When earwax builds up too much, it may plug the ear canal, obstructing the passage of sound waves to the eardrum. As a result, hearing may become muted or diminished, or in extreme cases, lost entirely.
Having a narrow ear canal, wearing hearing aids, or creating too much earwax are all things that can make earwax buildup more likely. It’s crucial to remember that using cotton swabs or other things to try and remove earwax may instead push it deeper into the ear canal and result in more issues.
It is advised to refrain from introducing anything, including cotton swabs, into the ear canal in order to prevent earwax buildup and the ensuing hearing loss. Instead, a medical expert can use specialized tools to remove extra earwax in a safe manner.
-
Tips for preventing earwax buildup:
Hearing loss is frequently brought on by earwax buildup. Hearing that is muted or distorted can result from it blocking the passage of sound to the eardrum. A natural material called earwax guards against infection and foreign objects in the ear canal. However, if it accumulates, it may get obstructed and result in hearing issues.
Avoid placing things into the ear canal, such as cotton swabs or hairpins, as they can push earwax deeper into the ear, leading to earwax buildup and potential hearing loss. Additionally, it’s critical to maintain the ear canal clean by using ear drops to dissolve earwax or gently wiping the outer ear with a washcloth.
It’s crucial to seek medical counsel from a healthcare provider if you have hearing loss or discomfort. Any excessive earwax can be safely removed, and they can also offer advice on how to avoid earwax buildup in the future.
Diseases that can cause hearing loss:
-
Explanation of how certain diseases can cause hearing loss:
Several things, including some disorders, can lead to hearing loss. While some illnesses can damage nerves and result in hearing loss, other disorders impact the inner ear. Hearing loss can be brought on by illnesses including meningitis, mumps, measles, and syphilis, especially in children. Hearing loss is a problem that can also be influenced by other health issues like diabetes and high blood pressure. Hearing loss is occasionally a side effect of the drugs used to treat various illnesses. It’s crucial to manage these conditions and get medical help if you have any hearing issues. A potential hearing loss caused by underlying disorders can be identified and managed with regular checkups and conversation with healthcare professionals.
-
Examples of diseases that can cause hearing loss:
Many illnesses and medical problems can lead to hearing loss. Meniere’s disease, which affects the inner ear and can result in vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss, is one typical case. The abnormal growth of bone in the middle ear known as otosclerosis is another condition that can cause hearing loss. If left untreated, chronic ear infections like otitis media can also result in hearing loss. Autoimmune conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis are among the other illnesses that can result in hearing loss. Additionally, meningitis and other illnesses that cause high fevers can harm the auditory nerve and cause hearing loss. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you have any signs of hearing loss or a medical condition that could make them worse.
-
Tips for preventing diseases that can cause hearing loss:
Many illnesses, including meningitis, measles, mumps, and others, can lead to hearing loss. If these illnesses are not treated right away, hearing loss may become permanent. To avoid such disorders, it is crucial to adopt preventive steps. The greatest method for preventing illnesses that can lead to hearing loss is vaccination. Aside from regular checkups, early disease detection can also aid in preventing hearing loss. The likelihood of contracting such diseases can also be decreased by practicing excellent hygiene and leading a healthy lifestyle. The general health of a person can be enhanced and diseases prevented by frequently washing hands, avoiding close contact with infectious individuals, and eating a healthy diet. It is crucial to adhere to these straightforward suggestions to safeguard oneself from illnesses that can cause hearing loss and maintain excellent health.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a number of factors, such as age, noise exposure, heredity, some medications, infections and diseases, head and ear injuries, and earwax buildup, can contribute to hearing loss. To avoid hearing loss and preserve excellent hearing health, it’s critical to understand the causes of hearing loss.
Avoiding exposure to loud noises, using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones to protect your ears, obtaining frequent hearing checks, addressing prescription side effects with your doctor, and properly cleaning your ears can all help prevent hearing loss.
It’s crucial to take extra care to protect your hearing if you have a family history of hearing loss or are at risk for certain disorders that might cause hearing loss.
Overall, maintaining good hearing health and enhancing your quality of life can be achieved by being aware of the causes of hearing loss and implementing measures to avoid them.
F A Q:
- What causes hearing loss most frequently?
A: Presbycusis, or hearing loss associated to ageing, is the most typical cause of hearing loss. - How can I stop hearing loss brought on by ageing?
A: Regular hearing exams and the use of hearing protection in noisy settings can help you avoid age-related hearing loss. - What is hearing loss brought on by noise?
A: Prolonged exposure to loud noise, such as that produced by machinery, music, or weapons, results in noise-induced hearing loss. - What kinds of situations can lead to hearing loss due to noise?
A: Noise-induced hearing loss can occur in settings including concerts, athletic events, and construction sites. - How can I stop hearing loss brought on by noise?
A: When in noisy surroundings, you can avoid hearing loss due to noise by wearing earplugs or earmuffs.
Remember, that it’s important to get medical attention right away if you notice any changes in your hearing. You can read more here
https://onehearingaid.com/hearing-aids-price/
https://onehearingaid.com/latest-hearing-aids-in-2023/
You can follow us on Twitter for more updates: https://twitter.com/onehearingaid?t=kUKzkxIECwM2lEmz3R_K7Q&s=03

3 thoughts on “8 Causes of hearing loss?”