Beyond traditional hearing aids! Discover a range of Hearing Aid Alternatives to empower your hearing journey. Explore options like bone conduction devices, assistive listening systems, and more. Understand their strengths, limitations, and suitability for different hearing loss types. Gain valuable insights and resources to make informed decisions about your hearing health. Don’t let hearing loss hold you back – chart your course toward clearer communication and a vibrant world of sound!
Introduction:
Imagine struggling to catch conversations with loved ones, missing movie punchlines, or feeling isolated in social settings. This is the reality for millions worldwide who experience hearing loss. While traditional hearing aids offer a familiar solution, they may not be the perfect fit for everyone.
This post dives into the exciting world of hearing aid alternatives. Get ready to discover a range of options tailored to your unique needs and preferences. Whether you seek an affordable solution, prioritize natural sound quality, or have specific listening challenges, there’s something here for you.
By exploring these alternatives, you’ll be empowered to make informed decisions and take control of your hearing health. So, let’s embark on this journey together and discover a world where clear communication and vibrant soundscapes are within reach!
Overview of Hearing Loss and Hearing Aid Alternatives:
Hearing loss affects people of all ages and comes in various forms:
- Conductive: Sound waves have difficulty reaching the inner ear, often due to earwax buildup, middle ear infections, or a punctured eardrum.
- Sensorineural: Damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve hinders sound processing. This can be caused by aging, exposure to loud noises, certain medications, or genetic factors.
- Mixed: A combination of both conductive and sensorineural factors.
- Presbycusis: Age-related hearing loss, affecting high-frequency sounds first.
Beyond Traditional Hearing Aids:
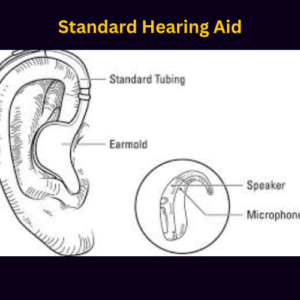
While traditional hearing aids amplify sound for many, they might not be the ideal solution for everyone. The good news is there are exciting alternatives:
- Affordability: Some alternatives offer lower initial costs or require less frequent upgrades.
- Customization: Certain options cater to specific listening environments or preferences.
- Specific Needs: Some alternatives address the limitations of traditional hearing aids, like bone conduction for conductive loss.
Exploring the Possibilities:
The journey towards better hearing doesn’t have to be a one-size-fits-all approach. Traditional hearing aids, while valuable, may not always be the perfect fit. This post unveils a diverse spectrum of alternatives, each catering to specific needs and preferences:
For the Cost-Conscious:
- Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs): Affordable option amplifying sounds, but not FDA-regulated like hearing aids. Suitable for mild hearing loss or specific situations.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): Amplified phones, TV listening systems, and hearing loops enhance sound in specific environments.
For the Tech-Savvy:
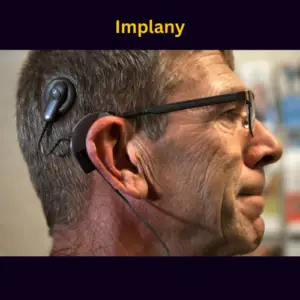
- Bone Conduction Devices: Transmit sound vibrations directly to the inner ear, bypassing the outer and middle ear. Ideal for conductive hearing loss and those seeking a natural sound experience.
- Cochlear Implants: Surgically implanted devices directly stimulate the auditory nerve, offering significant improvement for severe hearing loss.
For the Specific Needs:
- Auditory Training Programs: Retrain the brain to interpret sound more effectively, benefiting individuals with cochlear implants or auditory processing difficulties.
Remember:
- Each alternative has its strengths and limitations. Consider consulting a hearing healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
- This post provides a starting point. Further research each option to understand its suitability for your specific needs.
Ready to dive deeper into these exciting alternatives? Stay tuned as we explore each option in detail, empowering you to make informed decisions toward better hearing!
Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs):
Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs) have emerged as an alternative to traditional hearing aids, offering an often more affordable option for amplifying sounds. But before you jump on the PSAP bandwagon, let’s understand if they’re the right fit for your unique needs.
PSAPs vs. Hearing Aids: Know the Difference
PSAPs are not regulated as medical devices by the FDA, unlike hearing aids. This means they haven’t undergone the same rigorous testing and may not be suitable for addressing hearing loss. PSAPs simply amplify all sounds in the environment, whereas hearing aids personalize amplification based on your specific hearing profile and filter out background noise for improved clarity.
Who Can Benefit from PSAPs?
PSAPs might be suitable for:
- People with mild hearing loss: If you have difficulty hearing soft sounds in quiet environments, PSAPs could offer a helping hand. However, they won’t address the nuances of speech understanding or filter out background noise in complex listening situations.
- Specific listening situations: If you enjoy birdwatching, attending lectures, or need occasional amplification in specific environments, PSAPs can temporarily boost sounds.
Weighing the Pros and Cons:
Advantages:
That’s a great start! You’ve clearly outlined the advantages of PSAPs: cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and over-the-counter availability. To make the “Weighing the Pros and Cons” section even more informative, consider adding:
Additional advantages:
- Variety of styles and features: PSAPs come in various designs, from small in-ear models to headphone-style devices, catering to different preferences and comfort levels. Some offer features like volume control and tone adjustment.
- Portability and convenience: PSAPs are often compact and battery-powered, making them ideal for carrying around and using in various situations.
Limitations:
- Not suitable for all types of hearing loss: PSAPs are not recommended for moderate to severe hearing loss, as they cannot provide the necessary level of amplification and noise filtering.
- Potential for feedback: High amplification in certain environments can create a whistling sound (feedback) that can be uncomfortable and disruptive.
- May not improve speech understanding: While PSAPs amplify all sounds, they don’t have the technology to specifically enhance speech clarity, which is crucial for many people with hearing loss.
Overall:
PSAPs can be a viable option for individuals with mild hearing loss or those seeking occasional sound amplification in specific situations. However, it’s crucial to understand their limitations and consult a hearing healthcare professional to determine if they are the right fit for your individual needs and hearing loss profile.
Limitations:
- No noise filtering: PSAPs simply amplify all sounds, potentially making background noise even more bothersome.
- Potential for distortion: High amplification can distort sound quality, impacting clarity and comfort.
- Legal considerations: PSAPs are not medical devices and haven’t undergone the same safety and efficacy testing as regulated hearing aids.
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs):

Beyond hearing aids, Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) offer targeted solutions for enhancing sound in specific environments. Let’s explore various ALDs and how they can empower you to actively participate in conversations, lectures, and public spaces, despite hearing challenges.
Common ALDs and their functionalities:
- Amplified phones: These phones provide adjustable volume levels, making phone conversations clearer. Some models even offer features like noise reduction and speakerphone options for improved accessibility.
- TV listening systems: These systems connect wirelessly to your TV, transmitting sound directly to your hearing aid or headphones, often with adjustable volume and personalized settings.
- Hearing loops: Installed in public spaces like theaters, museums, and lecture halls, these loops transmit sound directly to hearing aids equipped with a telecoil (t-coil) setting, eliminating background noise and improving clarity.
- Personal FM systems: These portable systems consist of a microphone worn by the speaker and a receiver worn by the listener. They offer clear sound even in noisy environments, perfect for one-on-one conversations or small group settings.
Benefits of ALDs in different settings:
- Conversations: Amplified phones and personal FM systems can significantly improve speech understanding in noisy restaurants, cafes, or even during walks with friends.
- Lectures and meetings: Hearing loops and TV listening systems ensure you don’t miss crucial information in lecture halls, conference rooms, or while watching presentations.
- Public spaces: Hearing loops in theaters, museums, and transportation hubs allow you to fully engage with the environment, enjoying movies, exhibits, or announcements without straining to hear.
Compatibility and limitations to consider:
- ALD compatibility: Ensure your hearing aid has features like a t-coil or Bluetooth connectivity for compatibility with specific ALDs.
- Environmental dependence: Hearing loops and some personal FM systems require specific infrastructure or proximity to the sound source.
- Limited portability: Some ALDs like TV listening systems are primarily for home use, while others offer portable options.
Bone Conduction Devices:
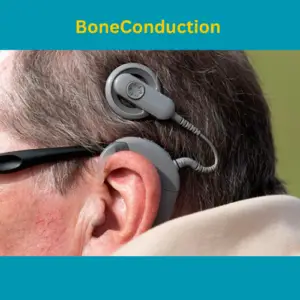
Sound bypasses your outer and middle ear, reaching your inner ear directly through bone vibrations. That’s the magic of bone conduction devices, offering a unique solution for specific hearing loss types. Let’s dive deeper into this innovative technology and see if it holds the key to improved hearing for you.
Hear through Your Bones:
Unlike traditional hearing aids that amplify sound through the ear canal, bone conduction devices (BCDs) take a different route. They transmit sound vibrations through the cheekbone directly to the cochlea, your inner ear’s sound-receiving organ. This bypasses any blockages in the outer or middle ear, making them particularly suitable for certain types of hearing loss.
Who Benefits from BCDs?
If you have conductive hearing loss or mixed hearing loss with a conductive component, BCDs could be a game-changer. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves have difficulty reaching the inner ear due to issues in the outer or middle ear, such as earwax buildup, middle ear infections, or a perforated eardrum. BCDs bypass these blockages, delivering sound directly to the inner ear.
Why Choose BCDs?
Several advantages make BCDs an attractive option:
- Comfort: No need for ear inserts, ensuring comfort and preventing ear infections common with traditional hearing aids.
- Situational awareness: You can still hear ambient sounds, making them ideal for activities like cycling or having conversations while wearing them.
- Open design: Allows you to enjoy natural sound quality and be aware of your surroundings.
But are BCDs the perfect solution for everyone?
Like any technology, BCDs have limitations:
- Cost: BCDs can be more expensive than traditional hearing aids.
- Sound quality: While improving, sound quality may not match traditional hearing aids for all users, especially for music appreciation.
- Not suitable for all: They primarily benefit individuals with conductive or mixed hearing loss, not sensorineural hearing loss affecting the inner ear itself.
Remember:
Consulting a hearing healthcare professional is crucial to determine if BCDs are right for you. They can assess your specific hearing needs and recommend the most suitable solution, whether BCDs, traditional hearing aids, or a combination of both.
Cochlear Implants
:
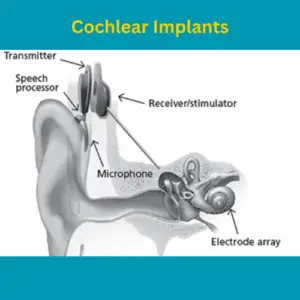
Cochlear implants, marvels of modern technology, offer a beacon of hope for individuals with severe hearing loss. By directly stimulating the auditory nerve, they bypass damaged parts of the inner ear and pave the way for a renewed connection to the world of sound. Let’s delve into the world of cochlear implants, exploring their eligibility criteria, surgical process, and the life-changing benefits they can bring.
Understanding Cochlear Implants:
Unlike traditional hearing aids that amplify sound, cochlear implants take a different approach. They surgically implanted devices containing an electrode array. This array directly stimulates the auditory nerve, bypassing damaged hair cells in the inner ear that prevent sound reception in severe hearing loss.
Who Can Benefit?
If you have severe sensorineural hearing loss, meaning significant damage to the inner ear, and haven’t found sufficient benefit from traditional hearing aids, cochlear implants might be an option. However, several factors determine eligibility, including:
- Age: Implants are often suitable for adults and older children who meet specific criteria.
- Overall health: Good general health is crucial for undergoing the surgery.
- Motivation and commitment: The recipient needs to be actively involved in rehabilitation and speech therapy for optimal results.
The Surgical Journey:
The cochlear implant surgery is delicate but typically safe. A qualified surgeon places the implant device under the skin behind the ear and carefully inserts the electrode array into the cochlea. The surgery usually takes a few hours, and recovery involves following specific instructions and attending follow-up appointments.
Life After Activation:
Once the implant is activated, a new auditory experience begins. The sound initially might seem unfamiliar, but with dedicated rehabilitation and speech therapy, the brain learns to interpret the electrical signals, gradually restoring speech understanding and appreciation of various sounds.
Potential Benefits:
Cochlear implants can:
- Significantly improve speech understanding: This allows individuals to engage in conversations with increased clarity and confidence.
- Enhance quality of life: Reconnecting with the world of sound can have a profound impact on social interactions, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
- Restore access to sounds: Imagine hearing music, laughter, nature’s soundscapes, and everyday noises you might have missed due to hearing loss.
Remember:
Cochlear implants are a significant investment, both financially and emotionally. Consulting a hearing healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and discussing realistic expectations is crucial before making this life-changing decision.
Auditory Training Programs:

Our journey through hearing health alternatives wouldn’t be complete without exploring auditory training programs. These non-surgical interventions focus on retraining your brain to interpret sound more effectively, leading to improved listening skills and communication abilities. Let’s unlock the potential of auditory training and see if it holds the key to enhancing your hearing experience.
Retraining Your Brain to Hear:
Hearing loss isn’t just about damaged ears; sometimes, the brain struggles to process sound signals correctly. Auditory training programs provide targeted exercises designed to stimulate and strengthen the auditory pathways in the brain, helping it better analyze and interpret incoming sounds. Think of it as brain fitness for your hearing!
A Spectrum of Training Programs:
Different programs cater to varied needs and goals. Some common types include:
- Sound discrimination: These exercises help differentiate between similar sounds, improving speech clarity and understanding, especially in noisy environments.
- Auditory localization: By identifying the direction of sounds, these programs enhance spatial awareness and improve your ability to follow conversations in group settings.
- Tinnitus retraining therapy: Specifically designed for individuals with tinnitus (ringing in the ears), these programs help habituate the brain to the tinnitus sound, reducing its perceived loudness and impact on daily life.
Who Can Benefit?
Auditory training can be valuable for:
- Individuals with cochlear implants: By retraining the brain to interpret the new electrical signals from the implant, these programs accelerate adaptation and optimize speech understanding.
- People with auditory processing disorders (APD): Individuals with APD struggle to process auditory information efficiently. Training can improve their ability to filter background noise, understand rapid speech, and follow complex instructions.
- Anyone seeking to improve listening skills: Even those with mild hearing loss or age-related decline in auditory processing can benefit from training to enhance clarity and communication confidence.
Remember:
Auditory training isn’t a magic bullet, but it offers a safe and effective way to support your hearing health. Consulting a hearing healthcare professional for a personalized assessment and guidance on suitable training programs is crucial for maximizing its benefits.
Stay tuned for the final section:
We’ll wrap up our exploration of hearing aid alternatives by summarizing your options and emphasizing the importance of seeking professional guidance to navigate your unique hearing journey. Remember, empowered knowledge leads to informed decisions and improved hearing health!
Conclusion:
Navigating hearing loss doesn’t have to be a solo expedition. This exploration unveiled a diverse landscape of alternatives, each with its strengths and applications. But with so many options, where do you begin?
Remember, the ideal solution hinges on your unique needs, hearing loss type, lifestyle, and preferences. Let’s revisit some highlights:
- Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs): Affordable for mild loss or specific situations, but not a substitute for comprehensive hearing solutions.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): Amplify sound in specific environments, but rely on external systems and compatibility.
- Bone Conduction Devices (BCDs): Bypass blockages for conductive loss, offering comfort and situational awareness, but with cost and sound quality considerations.
- Cochlear Implants: A significant investment for severe loss, offering life-changing benefits, but requiring careful evaluation and realistic expectations.
- Auditory Training Programs: Retrain your brain to interpret sound effectively, benefiting those with implants, processing disorders, or anyone seeking to enhance listening skills.
The Key Ingredient: Professional Guidance
While this journey has equipped you with valuable knowledge, remember, that a hearing healthcare professional is your invaluable teammate. They can:
- Assess your unique needs: Understand your specific hearing challenges and lifestyle.
- Recommend suitable options: Guide you through cost, effectiveness, and compatibility considerations.
- Provide ongoing support: Ensure your chosen solution continues to serve you throughout your hearing journey.
Armed with knowledge and professional guidance, you can confidently navigate the world of alternatives and choose the path towards clearer communication, improved quality of life, and a vibrant connection to the world of sound. Remember, you’re empowered to embark on this journey – and you don’t have to walk it alone.
Additional Resources:
General Hearing Health Information:
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
- National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
Resources for Specific Hearing Aid Alternatives:
- Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs):
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs):
- Bone Conduction Devices (BCDs):
- Cochlear Implants:
- Auditory Training Programs:
Disclaimer:
This information is for general educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance on your hearing health.
Please Read More:
Understanding Unilateral Hearing Loss: Causes, Effects, and Coping Strategies

2 thoughts on “Hearing Aid Alternatives-Unveiling Your Path to Clearer Sound”