Hearing aids have become indispensable tools for individuals with hearing loss, amplifying sounds and enhancing communication. However, like any electronic device, hearing aids have a finite lifespan, raising the question of their longevity. This comprehensive guide delves into the factors that influence hearing aid longevity and provides insights into extending their lifespan.
Typical Lifespan of Hearing Aids
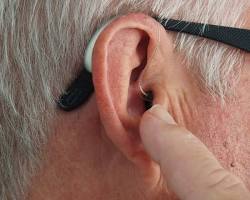
The typical lifespan of hearing aids generally ranges from three to seven years. This range is influenced by several factors, including the style of hearing aid, its maintenance, and the user’s lifestyle.
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids typically last for three to four years, while behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids may last for four to five years. Rechargeable hearing aids, on the other hand, have a longer lifespan, with lithium-ion batteries lasting up to four to five years.
Factors Affecting Hearing Aid Longevity
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the lifespan of hearing aids. These factors include:
- Style of Hearing Aid: ITE hearing aids are more susceptible to earwax buildup and moisture damage, leading to a shorter lifespan compared to BTE hearing aids.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and proper handling of hearing aids significantly extend their lifespan. Cleaning removes earwax, dirt, and debris, while careful handling prevents damage from drops or knocks.
- Lifestyle: Individuals with active lifestyles or those who frequently expose their hearing aids to harsh environments may experience a shorter lifespan due to increased wear and tear.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements in hearing aid design and features may lead to upgrades, prompting users to consider replacing their existing devices.
Signs Indicating Hearing Aid Replacement
Several signs indicate that it may be time to consider replacing your hearing aids. These signs include:
- Decreased Hearing Performance: If you notice a decline in your hearing ability despite consistent hearing aid usage, it may be a sign that your devices are no longer providing optimal amplification.
- Physical Damage: Cracks, dents, or corrosion on the hearing aid casings or components can compromise their functionality and necessitate replacement.
- Frequent Repairs: If your hearing aids require frequent repairs, it may be more cost-effective to replace them rather than continue incurring repair costs.
- Outdated Technology: If your hearing aids are several years old and lack advanced features, such as Bluetooth connectivity or noise cancellation, upgrading may provide significant benefits.
Extending the Lifespan of Hearing Aids
To extend the lifespan of your hearing aids, follow these tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean your hearing aids daily using a soft cloth and a mild cleaning solution provided by your audiologist.
- Moisture Protection: Store your hearing aids in a moisture-free environment when not in use, and consider using a dehumidifier if necessary.
- Removal During Water Activities: Remove your hearing aids before engaging in water activities to prevent water damage.
- Battery Care: Handle batteries with care, avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, and store them in a designated case.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your audiologist for professional cleaning, maintenance, and performance evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the signs that my hearing aids need to be replaced?
Decreased hearing performance, physical damage to the hearing aids, frequent repairs, and outdated technology are all indications that your hearing aids may need to be replaced.
- How can I extend the lifespan of my hearing aids?
Regular cleaning, moisture protection, battery care, and regular checkups with your audiologist are essential for extending the lifespan of your hearing aids.
- How often should I have my hearing aids checked?
It is recommended to have your hearing aids checked by your audiologist every six to twelve months.
- What are the different styles of hearing aids?
The three main styles of hearing aids are behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), and completely-in-the-canal (CIC).
- How much do hearing aids cost?
The cost of hearing aids varies depending on the style, features, and manufacturer. However, in general, hearing aids can range in price from $1,000 to $6,000 per ear.

1 thought on “How Long Do Hearing Aids Last”