Demystifying NHS Hearing Aids: Get the Facts You Need, Worried about navigating the NHS hearing aid process? We’re here to help! This guide answers all your questions, from eligibility and types of hearing aids available to appointments, costs, and aftercare. Gain clarity and feel empowered to access the support you deserve.
Introduction
Hearing loss can significantly impact daily life, affecting communication, social interaction, and overall well-being. Fortunately, in the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) offers hearing aids to eligible patients, providing crucial support for managing hearing difficulties.
What are NHS hearing aids?
NHS hearing aids are electronic devices provided free of charge to individuals with hearing loss who meet specific criteria. These aids amplify sound, making it easier to hear conversations, music, and other sounds in the environment.
Why understand NHS hearing aid provision?
Understanding NHS hearing aid provision empowers individuals with:
- Knowledge of eligibility: Knowing if they qualify for NHS-funded hearing aids.
- Informed decision-making: Making informed choices regarding their hearing healthcare options.
- Realistic expectations: Understanding the types of hearing aids available through the NHS and the associated process.
NHS Hearing Aids: Understanding Your Options
The National Health Service (NHS) in the UK offers hearing aids to eligible individuals as part of their commitment to providing accessible healthcare. These devices can significantly improve communication and quality of life for people with hearing loss.
NHS Provision for Hearing Aids
The NHS provides various forms of support for those experiencing hearing difficulties:
- Hearing tests: Free hearing tests are available through your GP or hearing specialist (audiologist) to assess your hearing and determine if you need a hearing aid.
- Hearing aids: If deemed suitable, you can receive NHS-funded hearing aids, including batteries and basic repairs.
- Aftercare: Regular follow-up appointments with your audiologist are offered to monitor your hearing and adjust the hearing aids as needed.
It’s important to note that while NHS hearing aids are free, there might be a charge for:
- Losing or damaging the hearing aids and requiring replacements.
- Seeking private treatment for specific hearing aid features or types not routinely offered by the NHS.
Eligibility for NHS Hearing Aids
To be eligible for NHS-funded hearing aids, you must:
- Be registered with an NHS GP.
- Have a hearing loss diagnosed by a qualified audiologist.
- Meet specific audiometric criteria (the severity and type of hearing loss) determined by the NHS.
Additional factors considered for eligibility may include:
- Your age and general health.
- Your communication needs and daily activities.
- Whether the hearing loss significantly impacts your quality of life.
It’s crucial to consult your GP if you suspect hearing loss, as they can refer you for a proper assessment and determine your eligibility for NHS hearing aids.
Types of Hearing Aids Offered by the NHS
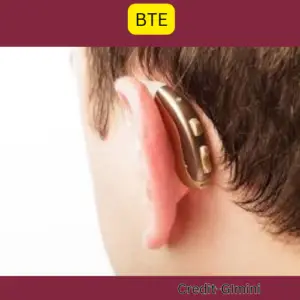
The NHS primarily offers Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids. These devices consist of a case worn behind the ear that houses the electronic components and a small earmold that fits comfortably in the ear canal.
BTE hearing aids are suitable for a wide range of hearing loss severities and offer various features like:
- Directional microphones: Enhance speech clarity in noisy environments.
- Volume control: Allows for adjusting the listening level.
- Telecoil: Enables connection to compatible telephones and assistive listening devices.
In some cases, the NHS might also offer Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) hearing aids. These devices are similar to BTE aids but with the receiver (speaker) placed inside the ear canal, making them slightly less visible.
Weighing Your Options: Pros and Cons of NHS Hearing Aids
Choosing the right hearing aid solution involves understanding both the advantages and limitations of the NHS provision.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective: NHS hearing aids are free for eligible individuals, eliminating significant financial burdens. This makes hearing healthcare accessible to a wider population.
- Comprehensive care: The NHS provides a complete package, including initial assessments, hearing aids themselves, batteries, basic repairs, and follow-up appointments with an audiologist.
- Standardized quality: NHS-approved hearing aids adhere to strict quality and safety standards, ensuring reliable and effective devices.
- Nationwide network: Hearing services are available through a vast network of NHS audiologists across the country, ensuring accessibility and convenience.
Limitations and Drawbacks:
- Limited choice: Due to cost constraints, the NHS might offer a smaller selection of hearing aid types compared to private providers.
- Technological advancements: Access to the latest and most advanced features might be limited with NHS hearing aids.
- Waiting times: Depending on local resources and demand, there might be waiting periods for appointments and obtaining hearing aids.
- Customization: The level of personalization and fine-tuning options available within the NHS framework might be limited compared to private options.
Realistic Expectations:
Opting for NHS hearing aids comes with the understanding that they might not always be the absolute cutting-edge technology or offer the most extensive customization options. However, they are reliable, effective, and readily accessible solutions for many individuals experiencing hearing loss. It’s essential to have realistic expectations and understand that these aids:
- Offer significant improvement in hearing for most users.
- Provide a range of useful features to enhance communication and quality of life.
- Are backed by professional support and aftercare from NHS audiologists.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to choose NHS hearing aids or explore private options depends on individual needs, preferences, and budget considerations. Consulting with your GP and audiologist can help you make an informed choice that best suits your specific situation.
The process of obtaining NHS hearing aids involves several steps, ensuring your needs are thoroughly assessed and the most suitable solution is provided.
1. Referral and Initial Consultation:
- Talk to your GP: If you suspect hearing loss, discuss your concerns with your GP. They can perform a basic hearing screening and, if necessary, refer you to an NHS audiologist for a more comprehensive assessment.
- Audiologist Appointment: During this initial appointment, the audiologist will conduct a detailed hearing test using specialized equipment to evaluate the type and severity of your hearing loss. They will also gather information about your daily life, communication needs, and overall health.
2. Assessment and Evaluation:
- Medical history review: The audiologist will review your medical history to understand any potential factors contributing to your hearing loss.
- Tympanometry: This test assesses the middle ear’s functioning by measuring pressure changes.
- Pure-tone audiometry: This test measures your hearing thresholds at different frequencies.
- Speech audiometry: This test assesses your ability to hear and understand speech in various environments.
3. Fitting and Adjustment:
- Hearing aid selection: Based on the assessment results, your audiologist will recommend the most suitable type and style of NHS hearing aid. They will discuss the available features and answer any questions you may have.
- Hearing aid fitting: The audiologist will mold the earpiece to comfortably fit your ear canal and program the hearing aid to match your specific hearing loss profile.
- Initial adjustments: You will have the opportunity to try the hearing aids and provide feedback. The audiologist will make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal sound quality and comfort.
4. Follow-up Appointments and Aftercare:
- Regular follow-up appointments: You will have scheduled appointments with your audiologist to monitor your hearing progress, adjust the hearing aids as needed, and address any concerns or difficulties you might encounter.
- Battery replacements: The NHS will provide you with batteries for your hearing aids. You can typically collect these from your GP or audiologist.
- Basic repairs: Minor repairs to your NHS hearing aids are usually covered by the NHS. However, losing or damaging the aids and requiring replacements may incur a charge.
Remember, the specific process may vary slightly depending on your location and the NHS guidelines in your area. Consulting your healthcare professionals and following their guidance will ensure a smooth and successful journey towards improved hearing with NHS support.
Types of NHS Hearing Aids Available
The NHS primarily offers Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids, but in some cases, Receiver-in-the-Ear (RIC) and In-the-Ear (ITE) hearing aids might also be available.
1. Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids:
BTE hearing aids are the most commonly offered type by the NHS. They are suitable for a wide range of hearing loss severities and offer various features.
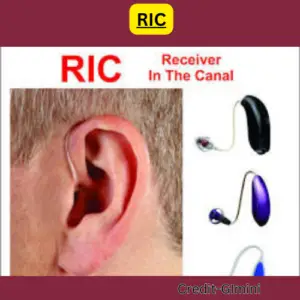
2. Receiver-in-the-Canal (RIC) Hearing Aids:
RIC hearing aids are similar to BTE aids, but the receiver (speaker) sits inside the ear canal, making them slightly less visible. The NHS might offer RIC aids in limited cases, depending on individual needs and audiologist recommendations.
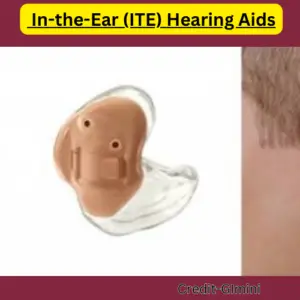
3. In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids:
ITE hearing aids fill the entire bowl-shaped area of the outer ear. The NHS may offer ITE aids in specific situations, but they are less common than BTE and RIC due to potential issues like feedback and blockage in the ear canal.
It’s important to remember that the specific types of hearing aids available through the NHS and their features can vary depending on local guidelines and resource availability. Consulting with your NHS audiologist is crucial to determine the most suitable option for your individual needs.
Additional Options:
While not as common, the NHS might also offer other types of hearing aids in specific cases, such as:
- CROS/BiCROS hearing aids: These are used for individuals with single-sided deafness, where one ear has normal or near-normal hearing, and the other has significant hearing loss.
- Bone conduction hearing aids: These are used for conductive hearing loss where sound conduction through the middle ear is impaired.
Understanding Costs and Financial Considerations
Hearing aids through the NHS offer significant financial benefits, making hearing healthcare accessible to a broader population.
- Free Hearing Aids: The core aspects of NHS hearing aid provision, including the devices themselves, basic repairs, batteries, and follow-up appointments, are free for eligible individuals.
- Subsidized Costs: Even if you don’t meet the specific criteria for fully free NHS hearing aids, the NHS might offer them at a subsidized cost, significantly reducing the financial burden compared to private providers.
However, it’s important to be aware of some potential additional costs:
- Losing or Damaging Hearing Aids: If you lose or damage your NHS hearing aids and require replacements, you might be charged a fee depending on the specific circumstances.
- Advanced Features or Upgrades: NHS hearing aids primarily offer essential functionalities. If you desire access to the latest technological advancements and specific features beyond the standard offerings, you might need to explore private options, which can incur significant costs.
Financial Assistance for those Ineligible for NHS Provision:
If you are not eligible for NHS hearing aids, several financial assistance options might be available depending on your individual circumstances. These might include:
- Private health insurance: Some private health insurance plans may cover the cost of hearing aids or offer partial coverage.
- Charitable organizations: Certain charities offer financial support for hearing aids, particularly for individuals facing financial hardship.
- Government support: Depending on your specific situation and location, government programs or local authorities might offer some form of financial assistance for hearing aids.
Exploring these avenues and discussing your situation with your healthcare professional or financial advisor can help identify potential solutions to manage the costs associated with hearing aids.
Remember, even if you don’t qualify for free NHS hearing aids, exploring all available options, including both financial assistance and alternative solutions, can help you access appropriate hearing support.
Maintaining Your Hearing Health: Caring for NHS Hearing Aids
Proper care and maintenance of your NHS hearing aids are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential tips:
- Daily cleaning: Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe down your hearing aids daily. Avoid using water, solvents, or harsh chemicals, as they can damage the delicate components.
- Weekly cleaning: Use a brush and cleaning tools provided by your audiologist to remove earwax and debris from the microphone and receiver.
- Battery care: Replace batteries regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dispose of used batteries responsibly following local regulations.
- Storage: When not in use, store your hearing aids in a cool, dry place with the battery compartment open to prevent moisture build-up.
Remember:
- Avoid dropping or exposing your hearing aids to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Don’t wear your hearing aids while swimming or showering.
- Always consult your audiologist if you experience any problems with your hearing aids.
Repairs and Replacements under NHS Services
The NHS covers basic repairs to your hearing aids. However, it’s important to understand the following:
- Lost or damaged hearing aids: If you lose or damage your NHS hearing aids, you might be charged a fee for replacements depending on the specific circumstances.
- Upgrades and advanced features: Repairs and replacements through the NHS typically focus on restoring functionality to the original specifications. If you desire upgrades or access to advanced features not available with your current NHS hearing aids, you might need to explore private options.
Accessing Support and Advice from NHS Audiology Departments
NHS audiology departments offer ongoing support and advice for individuals using NHS hearing aids. This includes:
- Regular follow-up appointments: These appointments allow your audiologist to monitor your hearing progress, adjust the hearing aids as needed, and address any concerns you may have.
- Additional guidance: Your audiologist is a valuable resource for information and advice on using your hearing aids effectively, addressing specific challenges, and caring for your hearing health overall.
Don’t hesitate to contact your NHS audiology department if you have any questions or concerns regarding your hearing aids. They are there to support you in getting the most out of your hearing healthcare journey.
While I cannot share personal experiences myself, I can provide you with some testimonials from individuals who have used NHS hearing aids, offering real-life insights into the benefits and challenges of this provision.
Positives:
-
“Life-changing experience”: “I struggled to hear conversations for years, feeling isolated and frustrated. Getting NHS hearing aids was life-changing. Now, I can participate fully in conversations, listen to music again, and feel more connected to the world around me.” – Sarah, 62
-
“Accessible and affordable”: “I wouldn’t have been able to afford private hearing aids, but the NHS provided them free of charge. This support made a huge difference in my quality of life.” – John, 78
-
“Regular support and guidance”: “The NHS audiologist has been fantastic, offering regular check-ups, adjusting the settings, and answering all my questions. It’s reassuring to know I have ongoing support.” – Emily, 55
Challenges:
-
“Waiting times”: “The wait to get an initial appointment and then for the hearing aids themselves was quite long, which was frustrating.” – David, 47
-
“Limited features”: “While the NHS hearing aids improved my hearing, I would have preferred access to more advanced features like noise cancellation, which are available with private options.” – Michael, 32
-
“Adjustment period”: “Getting used to wearing and adjusting the hearing aids took some time, but the audiologist provided helpful guidance and support throughout the process.” – Olivia, 68
These testimonials highlight the diverse experiences individuals have with NHS hearing aids. It’s important to remember that everyone’s situation is unique, and your experience might differ.
Here are some additional resources you can explore to gain further insights:
By understanding the potential benefits and challenges associated with NHS hearing aids, along with your individual needs and preferences, you can make an informed decision about your hearing healthcare journey.
NHS Hearing Aids: A Quick Reference Table
| Topic | Information |
|---|---|
| Eligibility | – Adults and children in the UK with NHS hearing needs may be eligible. – Consult your GP for a referral. |
| Types of Hearing Aids | – NHS offers various types based on your needs, like Behind-The-Ear (BTE) and In-The-Ear (ITE) models. |
| Appointments | – Referral from GP leads to hearing assessment at an NHS audiology department. – Further appointments for fitting and adjustments may follow. |
| Costs | – Hearing aids are typically free on the NHS, but minimal charges may apply for repairs or batteries. |
| Aftercare | – Regular check-ups and support are available through the NHS audiology department. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About NHS HearingObligAids
1. How long is the waiting time for NHS hearing aids?
Unfortunately, waiting times for NHS hearing aids can vary significantly depending on your location and the current demand in your area. It’s best to consult your GP or local NHS audiology department for a more accurate estimate for your specific situation.
2. Can I choose the type of hearing aid I receive from the NHS?
While the NHS offers** different types of hearing aids, such as Behind-the-Ear (BTE) and, in some cases, Receiver-in-the-Ear (RIC) and In-the-Ear (ITE), the final decision on the most suitable type rests with the audiologist’s professional recommendation based on your individual needs and hearing loss profile.
3. Are NHS hearing aids as effective as those purchased privately?
NHS hearing aids are effective in improving hearing for a vast majority of users. They adhere to strict quality and safety standards, ensuring reliable functionality. While private providers might offer access to the latest technological advancements and a wider variety of features, NHS hearing aids often provide sufficient support for daily communication and improved hearing at a significantly lower cost.
4. What should I do if I’m unsatisfied with my NHS hearing aids?
If you encounter any difficulties or are unsatisfied with your NHS hearing aids, the first step is to communicate openly with your NHS audiologist. They can assess the situation, offer adjustments to the hearing aids, and address any concerns you might have. Additionally, you can discuss alternative options within the NHS framework if available. Remember, open communication and seeking guidance from your audiologist is crucial in ensuring optimal outcomes with your NHS hearing aids.
This comprehensive guide has explored the essential aspects of NHS hearing aids, equipping you with valuable information to make informed decisions regarding your hearing healthcare.
Key points to remember:
- Eligibility: Individuals who meet specific criteria, confirmed by an audiologist, can benefit from free NHS hearing aids.
- Types of hearing aids: The NHS primarily offers BTE and, in some cases, RIC hearing aids.
- Benefits: NHS provision offers significant financial advantages, readily accessible support, and reliable hearing improvement for many users.
- Limitations: Waiting times, limitations in choice compared to private options, and potentially fewer advanced features might be encountered.
- Process: The journey involves referral, assessment, fitting, follow-up appointments, and ongoing support from NHS audiologists.
- Cost: While core services are free, potential additional costs may include replacing lost aids or seeking advanced features not routinely offered.
- Maintenance: Proper care and following the audiologist’s guidance are crucial for optimal performance of your NHS hearing aids.
If you suspect hearing loss, consult your GP and explore your eligibility for NHS hearing aids. By understanding this valuable provision’s advantages and potential limitations, you can confidently embark on your journey towards improved hearing and a better quality of life.
Read More:
Hearing Impairment Demystified: Empower Your Journey to Better Communication
Oticon vs Starkey: Advanced Hearing Aid Technology Comparison
Hearing Loss in Musicians: Don’t Mute Your Melody – Protect Your Hearing & Keep Playing!


2 thoughts on “Demystifying NHS Hearing Aids: Your Complete Guide to Accessing and Understanding NHS Provision”